Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (5); September 25, 2019 [Booklet]![]()

Research Paper
Analysis of the post-partum vaginal repair by injecting platelet-rich plasma; a study undertaken in Saudi German hospital K.S.A.
Hassan Soliman HE-MAA
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(5): 122-125, 2019; pii:S225199391900019-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb19
Abstract
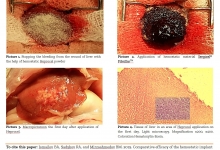
Aim. The research was based on the objective of vaginal recovery after vaginal delivery of women. PRP was used to determine whether the effects of the injecting PRP on vagina made any difference on vaginal prolapse repair or not. Therefore, the primary goal was to find the application of the PRP on the case of vaginal tear recovery of the mothers. Methods. The observational approach was utilized to conduct the following research. We examined (P=210) participants, while study duration was 10 months from November 2017 to August 2018. Results. The outcomes were 100% positive in the researcher’s cohort since all the participants responded well while recovered fast than the usual estimated time. Conclusion. Injecting PRP for repairing vaginal tear is considered to be optimizing for the general medical background patients whereas, for the long-term follow-up, the study requires to get the large numbers of participants in order to make the research generic.
Keywords: Post-Partum, Vaginal Tear, Vaginal Repair, Platelet-Rich Plasma, Gynecological Study
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Semantic Scholar]
Results of cytokine research of pregnant women with the risk of premature birth.
Khakimovna RN.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(5): 126-129, 2019; pii:S225199391900020-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb20
Abstract
Aim. The aim of the research is to study the content of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines of pregnant women with the risk of preterm birth (PB). Methods. Examined 42 women in the third trimester of gestation with the risk of preterm birth. Determination of the cytokine status of IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 and TNF-α in the serum of peripheral blood was performed by Enzyme immunoassay. Results. The systemic cytokine status was studied in pregnant women with the risk of PB. An imbalance of cytokines has been established, characterized by an increase in the content of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a decrease in anti-inflammatory interleukins, indicating an increased inflammatory response of the organism in the genesis of premature birth. Conclusion. The study of cytokine balance is important to assess the direction of the immune response, as well as the outcome of pregnancy for the mother and fetus. Excessive stimulation of the systemic humoral immune response as a result of increased activity of peripheral pro-inflammatory cytokines and low secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines are one of the fundamental mechanisms underlying the development of premature birth.
Keywords: Preterm birth, Pro-inflammatory, Anti-inflammatory cytokines, Cytokine status
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
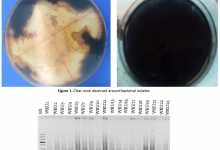
Assessment of antibacterial efficacy of Lugol's iodine compared with commercial hand sanitizers of Bangladesh.
Rahman Md.N, Abdullah-Al-Shoeb M, Huq S and Abul Kalam Azad M.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(5): 130-137, 2019; pii:S225199391900021-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb21
Abstract
Introduction. Hand disinfection is an essential step to prevent infection, reduce morbidity and minimize health care costs in a community. Aim. In this study, the Lugol's iodine (2%) solution was evaluated to use as an emergency hand sanitizer and compared with the three commercially available hand sanitizers (Hexisol, Sepnil and Handirub) of Bangladesh. Methods. These hand sanitizers were examined and analyzed by susceptibility test, minimum bactericidal concentration test and efficacy determination test. The agar diffusion test was used to assess the efficacy of the products against pathogenic Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Results. Handirub has inhibited all the test organisms with highest zones of inhibition ranging between 24.38 mm and 28.63 mm while Hexisol zone of inhibition was ranging from 13.3 mm to 15 mm. Unfortunately, Sepnil was inactive against Salmonella typhi, with very poor performance against other test organisms. All the three commercial hand sanitizers were only bacteriostatic at 100% concentration, while both 2% and 1% iodine were 100% bactericidal. The comparative study of the efficacy determination tests revealed that the Hexisol, Sepnil and Handirub are 93.05%, 85.99% and 96.57% effective against microorganism, respectively. Interestingly, both 2% and 1% of iodine solutions gave 100% reduction of viable bacteria during the efficacy determination test. Conclusion. It is concluded that 1% iodine showed better results against infection when compared to the other hand sanitizers used in this study. Recommendation. Lugol's iodine could be an effective alternative to hand washing to achieve asepsis for the health-care professional in emergency outreach program and water scarcity areas.
Keywords: Hand sanitizer, Lugol's iodine, Hand hygiene, Minimum inhibitory concentration
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
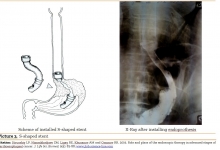
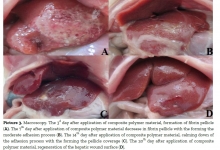
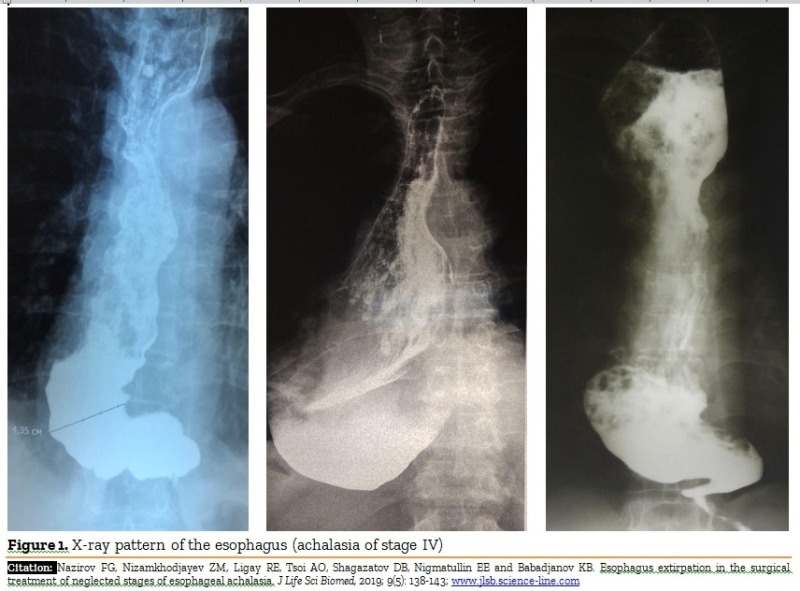
Esophagus extirpation in the surgical treatment of neglected stages of esophageal achalasia.
Nazirov FG, Nizamkhodjayev ZM, Ligay RE, Tsoi AO, Shagazatov DB, Nigmatullin EE and Babadjanov KB.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(5): 138-143, 2019; pii:S225199391900022-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb22
Abstract
Aim. The surgical treatment experience of patients with neglected stages of esophageal achalasia has been presented in the article. Methods. The esophagus extirpation with simultaneous gastroesophagoplasty due to esophageal achalasia of stage III-IV was performed in 28 patients. Results. The results of the research, identifies indications for surgical intervention, features of intra- and postoperative complications, immediate and long-term results of esophageal extirpation. Cardiodilation remains the main treatment method for patients with esophageal achalasia, but its efficiency is significantly reduced in patients with neglected stages. Conclusion. Esophagus extirpation in patients with neglected stages of achalasia is pathogenetically reasonable surgical intervention when there is severe esophagoectasia and S-shaped deformity of the esophagus and cardio-esophageal junction. Further control randomized trials and multicentric studies should be performed.
Keywords: Achalasia, Neuromuscular diseases of the esophagus, Esophageal extirpation, Gastroplasty.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Systematic review on avian immune systems
Birhan M.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(5): 144-150, 2019; pii:S225199391900023-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb23
Abstract
Aim. The aim of this review paper is too summarized and compares avian immune systems to the other domestic animals as comparative immunology type of review. Appreciation of the avian immune systems and their functions are very critical for disease diagnostics and new vaccine developments. Some of the avian immune systems are differ from mammalian immune systems, based on their production sources of immune cells like B-cells production site bursa of fabrics, but in mammalian is bone marrow. When we see the antibody type of birds; there are three principal classes of antibodies: IgM, IgG, IgY and IgA. Antibody diversity is achieved by gene re-arrangement. The other effector immune cell of birds is T cells. There are two distinct pathways that are α/β and γ/δ, avian T-cell diversity is probable made through combinatorial and junctional mechanisms. Recently, genes of several avian cytokines have been cloned and expressed. A number of naturally occurring viruses cause immunosuppression in chickens. Conclusion. There is much current interest in understanding the mechanisms of immunosuppression and developing strategies to enhance immune responsiveness in commercial poultry.
Keywords: Antibody, Avian, T cells, Vaccine
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]