Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
| Postbiotics and their role in healthy life |
Review
Postbiotics and their role in healthy life
Fesseha, H Yilma, T, E Mekonnen.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(4): 64-76, 2022; pii:S225199392200008-12
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.8 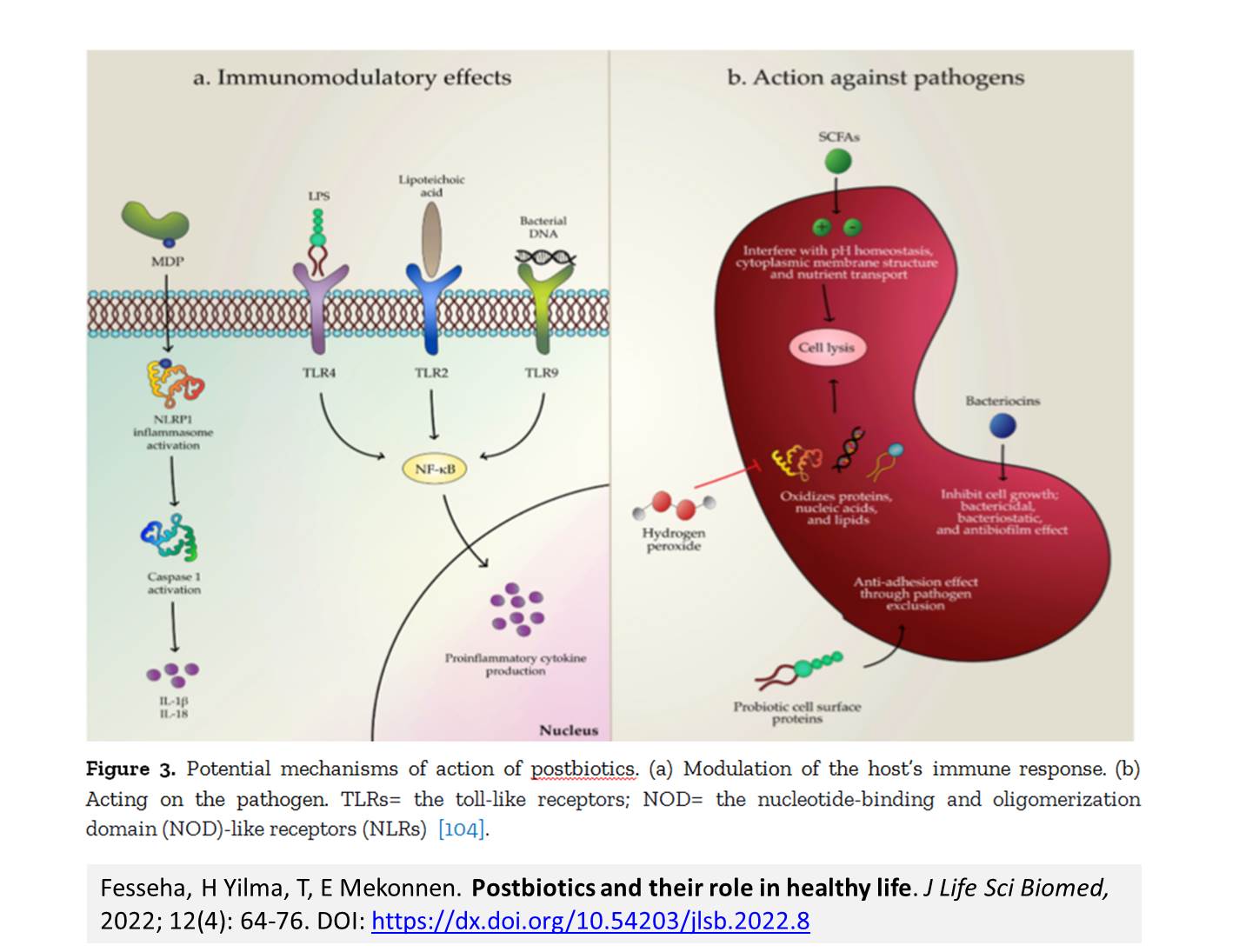
Abstract
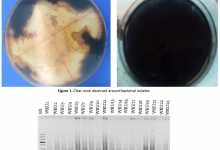
Introduction. Postbiotics refer to soluble factors (products or metabolic byproducts), secreted by live bacteria, or released after bacterial lysis, such as enzymes, peptides, teichoic acids, peptidoglycan-derived muropeptides, polysaccharides, cell surface proteins, and organic acids. These postbiotics have drawn attention because of their clear chemical structure, long shelf life, safety dose parameters, and the content of various signaling molecules which may have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-obesogenic, antihypertensive, hypo-cholesterolemic, anti-proliferative, and antioxidant activities. These properties suggest that postbiotics may contribute, to the improvement of host health by improving specific physiological functions, even though the exact mechanisms have not been entirely elucidated. It has been recognized that several mechanisms mediating the health benefits of beneficial bacterial cells do require viability. However, new terms such as para-probiotic or postbiotic have emerged to denote that non-viable microbial cells, microbial fractions, or cell lysates might also offer physiological benefits to the host by providing additional bioactivity. Aim. This review provides an overview of the postbiotic concept, evidence of their health benefits, and possible signaling pathways involved in their protective effects, as well as perspectives for applications in foods and pharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Postbiotic, Immunity, Health, Alternative treatment method, Therapeutic
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| RT-PCR test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs: results of the Cepheid Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay versus the Thermo fisher TaqPath™ COVID-19 CE IVD |
Research PaperCOVID-19
RT-PCR test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs: results of the Cepheid Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay versus the Thermo fisher TaqPath™ COVID-19 CE IVD
Zoungrana D, Rouamba SS, Nézien D, Sougué S, Kabré E.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(4): 77-81, 2022; pii:S225199392200009-12
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.9
Abstract
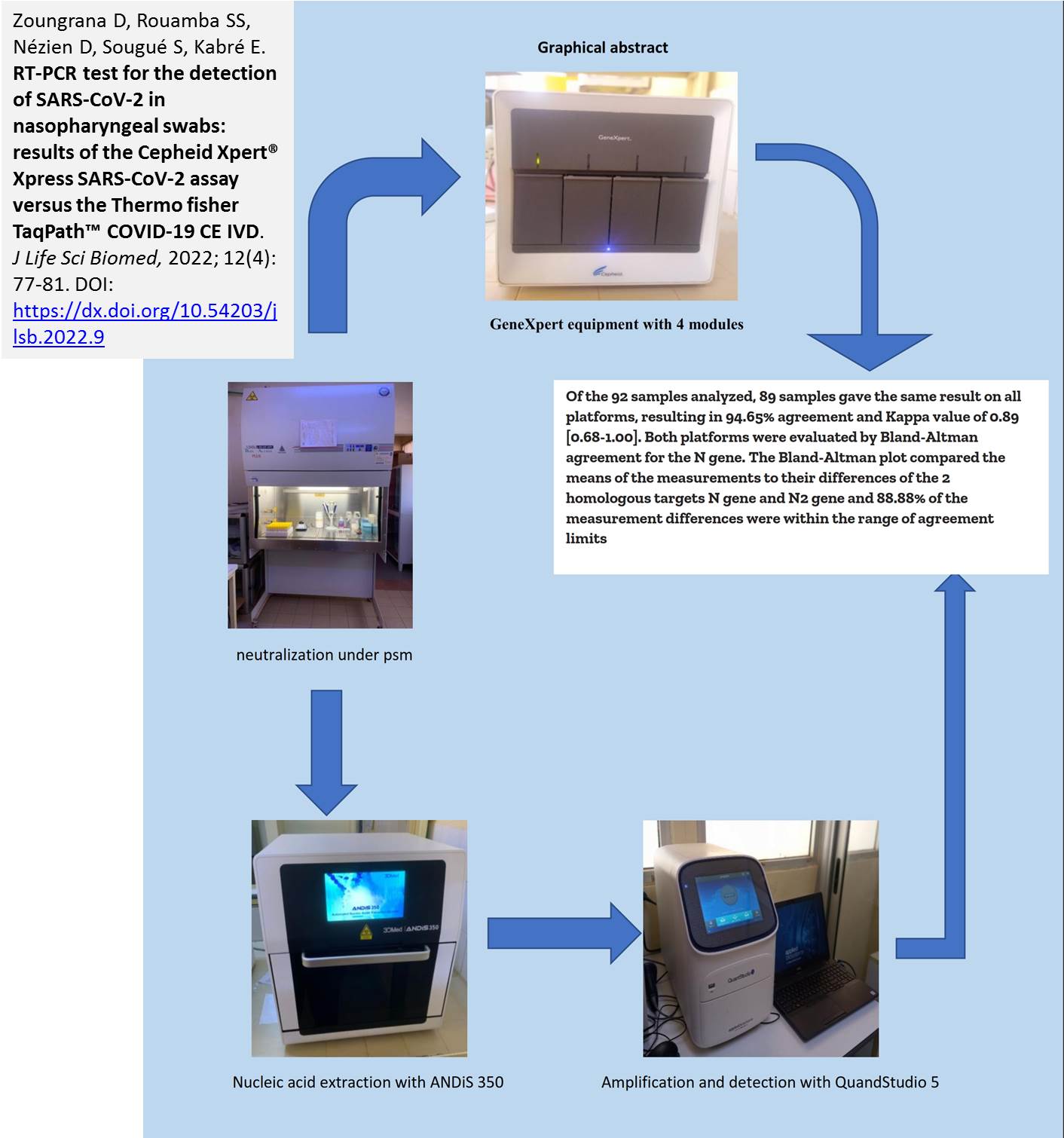
Introduction. In the response to the coronavirus pandemic, several PCR kits have been developed with varying performance. Aim. In this study, we compared the results of SARS-CoV-2 testing using the Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2 (Cepheid EUA) Testing with the TaqPathTM -COVID-19 CE IVD kit. Methods. A total of 92 nasopharyngeal swab samples from patients during September to November 2021 at the National Public Health Laboratory in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. These samples were analyzed using both the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay and the TaqPath-COVID-19-CE IVD kit on the QuantStudio 5 thermal cycler after extraction with the ANDiS 350 automated extractor. Results. The majority of patients was male 68.48% (63/92) and female 31.52% (29/92). The mean age was 42.2 ± 13.76 years with extremes of 12 and 70 years. The Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 kit showed positive agreement with a kappa coefficient of 93.35% [85.9; 100] compared to the TaqPath-COVID-19-CE IVD kit. It also showed a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 92.68 and negative and positive predictive values of 100% and 94.44% respectively. Conclusion. The Xpert Xpress test is a very simple assay that compares favorably with the TaqPath-COVID-19-CE IVD test and can be reliably used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal specimens.
Keywords: Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2, TaqPath-COVID-19-CE IVD, PCR, SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, ANDiS 350, QuantStudio 5
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)