Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 13 (4); December 25, 2023
Volume 13 (4); December 25, 2023
| Analysis of risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury in young children after cardiac surgery |
Research Paper
Analysis of risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury in young children after cardiac surgery
Ismailov SI, Khaydarov AE, Mamasiddikov SM, Narziev MZh, Khamraev GM, Nosirov RN, Sobirov DM, and Mardonov ZhN.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 13(4): 59-65, 2023; pii:S225199392300009-13
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2023.9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2023.9
Abstract
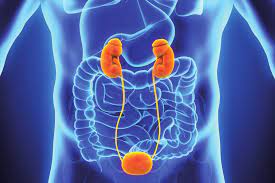
The aim of this study was to analysis of risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury (AKI) in young children with congenital heart disease (CHD) after cardiac surgery. The study included 137 young children with CHD after various types of cardiac surgery. The stages of AKI and indications for peritoneal dialysis (PD) were determined based of Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines. The incidence of AKI in young children in the general group was 40.9% (n=56). Stage 1 AKI was diagnosed in 21.9% (n=29) of patients, stage 2 AKI in 12.4% (n=17), and stage 3 AKI in 7.3% (n=10) of patients. Peritoneal dialysis was performed in 11.7% (n=16) of children. The incidence of AKI development after radical correct transposition of the great vessels (TGV) was 55.5% (n=5), truncus arteriosus (TA) was 100%, pulmonary atresia (PA)=25%, tetralogy of Fallot (TF)=38.1%, total anomalous pulmonary vein drainage (TAPVD)=60%, partial anomalous pulmonary vein drainage (PAPVD)=37.5%, atrioventricular canal (AVC)=44.4%, double outlet of main vessels from the right ventricle (DOMV from the RV)=60% , interventricular septal defect with high pulmonary hypertension (VSD)=21.6%, and combined operations was 46.6%. The need for PD after TGV correction was 22.2% (n=2), after TA=100%, after TF=33.3%, after TAPVD=20%, after AVC=11.1%, after VSD=1.9%, and after combined operations was 13.3%. Risk factors for AKI in young children were: younger age, initial heart failure, type of operation, prolonged cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and aortic clamping (AC), low cardiac output syndrome, inotropic and vasopressor therapy, hyperlactatemia. The development of AKI led to increased length of stay in the intensive care unit, overall hospitalization and infant mortality.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury, Children, Risk factors, AKI outcomes, Peritoneal dialysis.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Community based Integrated Enset bacterial Wilt (Xanthomonas Campestris pv. musacearum) management through collective actions in central Ethiopia region |
Research Paper
Community based integrated enset bacterial wilt (Xanthomonas Campestris pv. musacearum) management through collective actions in central Ethiopia region
Temam B, Getahun M, Kebede M, Tsegaye Y.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 13(4): 66-77, 2023; pii:S225199392300010-13
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2023.10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2023.10
Abstract
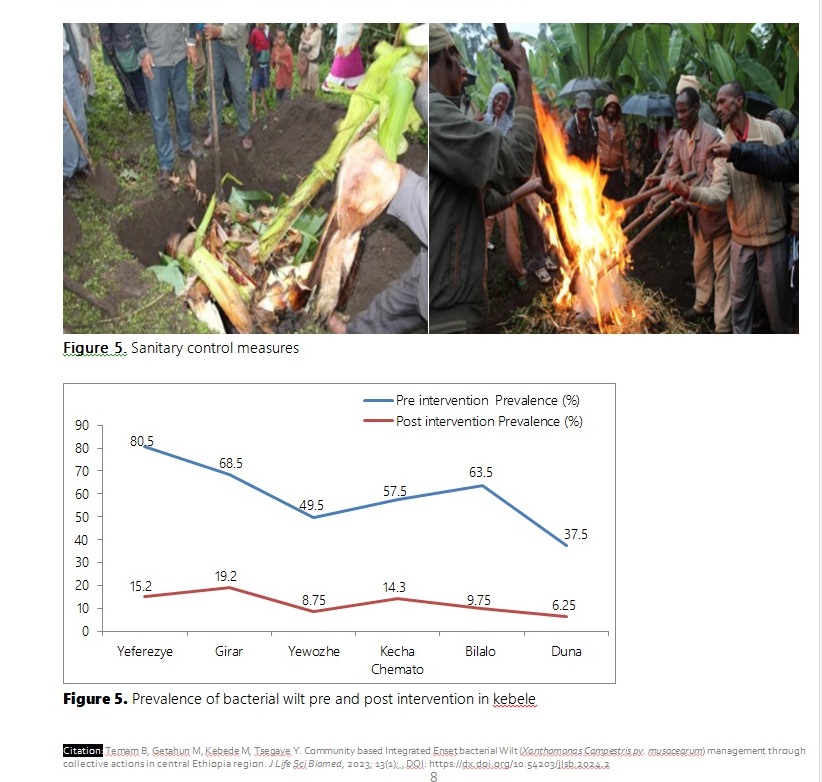
Enset ventricosum (Welw) Cheesman is an important food crop produced in southern part of Ethiopia and plays an important role in food security. However, the production of the crop is declines due to enset bacterial wilt disease caused by Xanthomonas campestris. Hence, the present study was designed with the aim of determining the epidemiology of bacterial wilt with the demonstration and dissemination of integrated disease management options in Mirab Azernet and Cheha district of central Ethiopia during the 2019-2021 growing season. Epidemiological information collected was using semi-structured designed questioners before and after intervention of integrated BW management. Natural epidemics of the disease showed a wide range of disease incidence at different plant growth stages. Based on a base line assessment, the average prevalence and incidence of three kebele in Cheha district were estimated to be 65.7% and 48.1% respectively, while the average prevalence and incidence of three selected kebele in Mirab Athernet were 52.8 and 36.9%, respectively. After intervention, the average prevalence of the disease was reduced to 5.6% in Mirab Azernet and to 10.1% in Cheha district. Sanitary control measures demonstrated the promising result in BW reduction. However, this traditional method of disease management option has not always the sustainable solution to alleviate the disease. To achieve a successful and sustainable bacterial wilt control measure, implementing IDM in enset farming community is the advisable approach to tackle the food insecurity of enset growers.
Keywords: Enset, Bacterial wilt, Incidence, Prevalence, Severity
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)