Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
| Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus among patients at university of Gondar hospital northwest Ethiopia: a retrospective study of 25870 cases |
Review
Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus among patients at university of Gondar hospital northwest Ethiopia: a retrospective study of 25870 cases
Belete D, Gashaw T, Belay S, Ambachew A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 01-10, 2025; pii:S225199392500001-15
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.1
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.1
Abstract
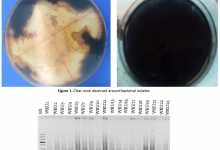
Emergence of antimicrobial resistance is a major public health problem worldwide, particularly in developing countries. The global spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) constitutes one of the most serious contemporary challenges to the treatment of hospital-acquired infections. The aim of this study was to determine the antimicrobial resistance pattern of Staphylococcus aureus isolate from different clinical specimens at University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital. A retrospective study used laboratory records of 25870 clinical specimens submitted for bacterial culture microbiology laboratory of University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital for bacterial culture and sensitivity testing from July 2018 and April 2022. Records from specimens positive for Staphylococcus aureus isolates were included for analysis. Standard bacteriological techniques were followed during culture preparation, sample collection, bacterial identification, and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Data was entered and analyzed using SPSS version 20. Of the total 25,870 samples culture records, 4653 (18%) were culture positive for bacteria. A total of 1057 S. aureus isolates were collected from clinical specimens such as: wound discharge (342; 32.4%), blood (312; 29.5%), cerebrospinal fluid (16; 1.5%), urine (21; 2%), other body fluids (71; 6.7%) and other discharge (295; 28 %). The prevalence of methicillin resistant S. aureus was 33.8% (233/698) and the overall prevalence of multi-drug resistant S. aureus out of 1057 S. aureus isolates was 36% (380/1057). We recommend further research on molecular studies evaluating the resistance genes and monitoring the epidemiology of multiple drug resistant S. aureus and MRSA.
Keywords: Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern, Staphylococcus aureus
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Pathomorphological features of the kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis with COVID-19 infection |
Research PaperCOVID-19
Pathomorphological features of the kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis with COVID-19 infection
Ibadov RA, Alimova HP, Yunusov AA, and Ibragimov SK.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 11-17, 2025; pii:S225199392500002-15
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.2
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.2
Abstract
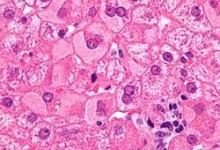
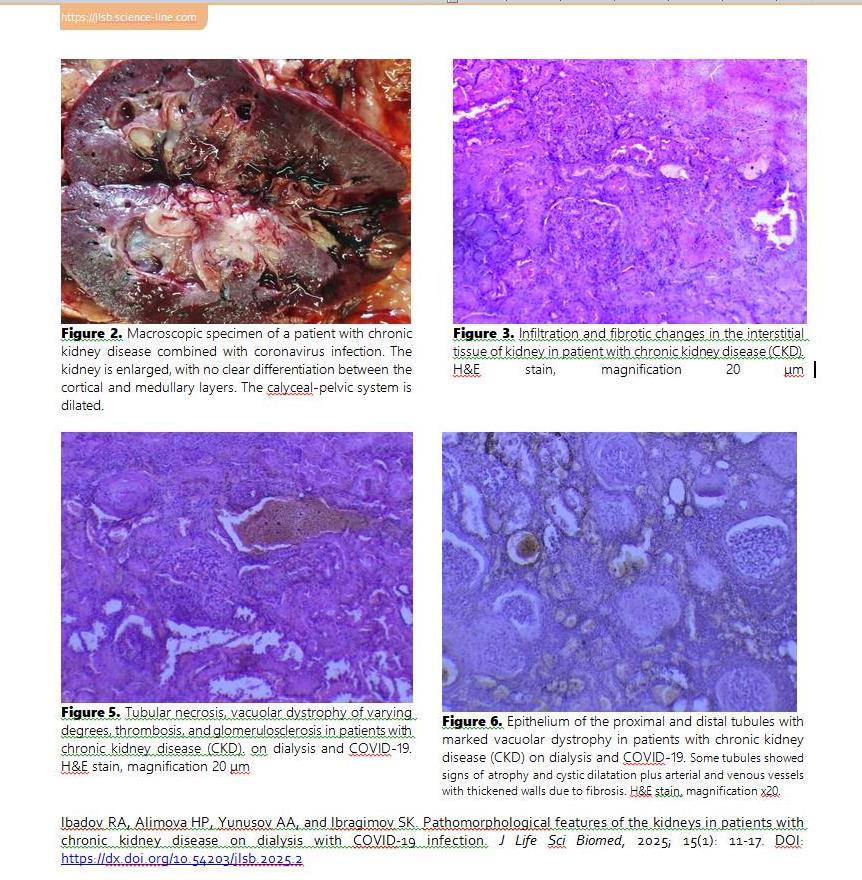
The current study aimed to investigate the pathomorphology of the kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis infected with COVID-19, focusing on structural changes and their correlation with the severity of the infection. The study included autopsy data from patients infected with COVID-19 who had been undergoing renal replacement therapy for 6 months to 1 year and died at the Zangiota Republican Specialized Center in 2022. The study was conducted using kidney biopsy samples. Morphological analysis included macroscopic examination, histological, and microscopic methods to identify signs of inflammation, fibrosis, and thrombosis. The results showed that kidneys of patients with COVID-19 were enlarged, with a granular surface and subcapsular hemorrhages. Histological examination revealed necrotic nephrosis, tubulointerstitial fibrosis, significant vascular involvement, and vacuolar degeneration of the tubules. Thrombosis of vessels and ischemic infarctions were frequently observed, correlating with the severity of COVID-19. The formation of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, associated with chronic inflammation, was a notable feature. COVID-19 induces significant pathological changes in the kidneys of patients with CKD on dialysis, aggravating the course of chronic kidney failure. It is concluded that there is a need for early detection and prevention of renal complications in patient with COVID-19.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease, COVID-19, Pathomorphology, Glomerulosclerosis, Dialysis.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Amiodarone-induced anaphylaxis in a Chihuahua: a case report |
Case Report
Amiodarone-induced anaphylaxis in a Chihuahua: a case report
Pehar B, Spahija N, Obhođaš M, and Maksimović A.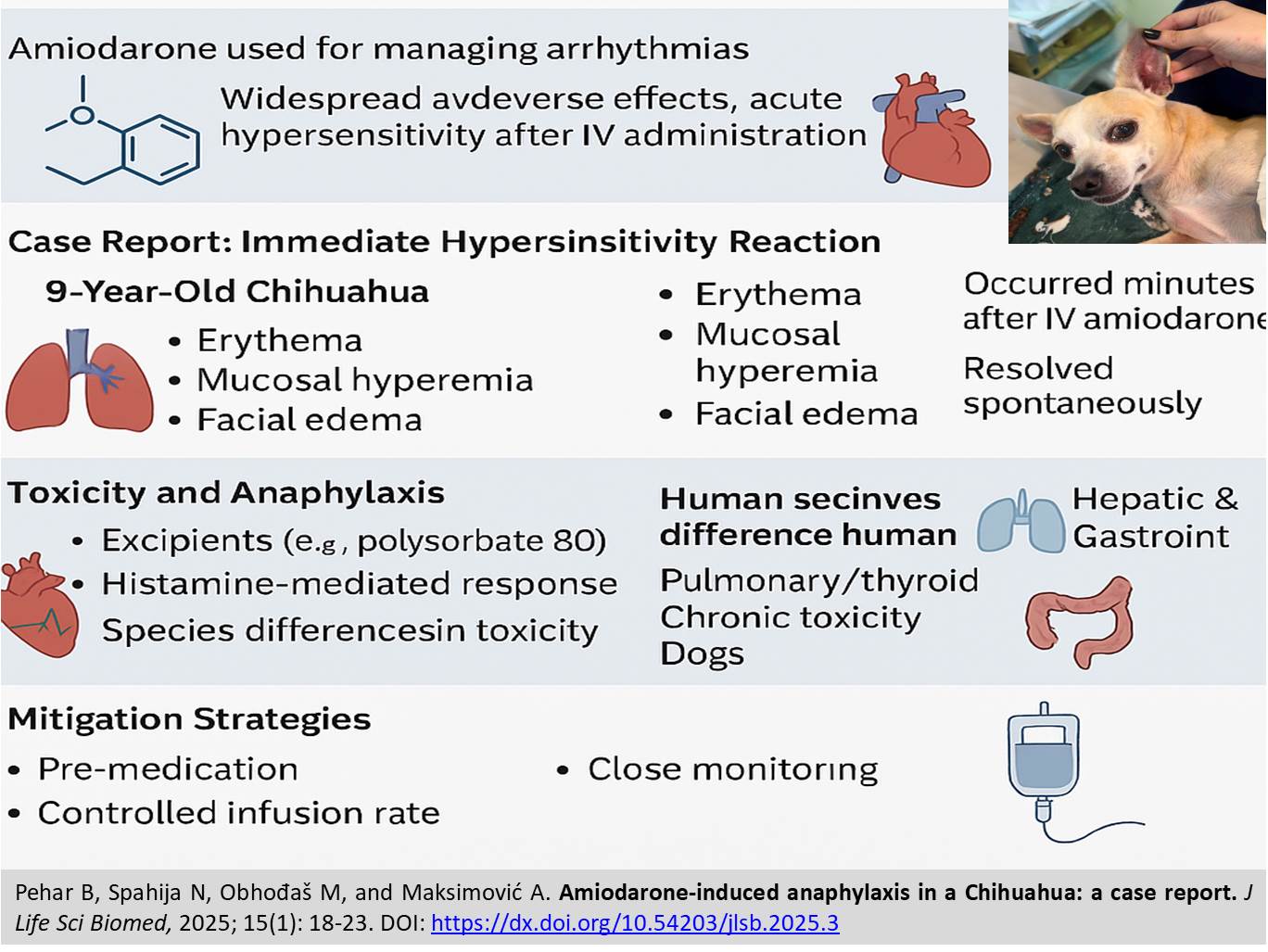 J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 18-23, 2025; pii:S225199392500003-15
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 18-23, 2025; pii:S225199392500003-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.3
Abstract
Amiodarone, a class III antiarrhythmic drug, is widely used in both human and veterinary medicine to manage ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. While its efficacy in rhythm control is well-established, the drug is associated with significant adverse effects, affecting multiple organ systems. In humans, amiodarone-induced toxicity commonly involves the pulmonary, hepatic, thyroid, and dermatological systems, with pulmonary toxicity being one of the most severe complications. Acute hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, are rare but have been reported, particularly in association with intravenous (IV) formulations containing polysorbate 80. In veterinary medicine, amiodarone is increasingly used to treat life-threatening arrhythmias in dogs, yet its safety profile is less extensively studied. Unlike humans, dogs appear to be more susceptible to immediate hypersensitivity reactions following IV administration, characterized by severe cutaneous signs, hypotension, and cardiovascular collapse. The present case report describes a 9-year-old Chihuahua that developed a rapid hypersensitivity reaction, including erythema, mucosal hyperemia, and facial edema, immediately after receiving IV amiodarone. The reaction resolved spontaneously within 15 minutes without requiring corticosteroid administration. Haematological and biochemical analyses showed a mildly decreased reticulocyte value, elevated neutrophil count, and increased ALT, while all other parameters were within reference ranges. A review of the literature suggests that excipients such as polysorbate 80 and benzyl alcohol may be primary contributors to amiodarone-induced anaphylaxis in dogs. Histamine-mediated responses, severe hypotension, and cardiovascular complications have been documented in both human and veterinary cases, with dogs displaying heightened sensitivity to IV administration. Additionally, while pulmonary and thyroid toxicity are well-recognized chronic effects in human patients, hepatic and gastrointestinal toxicities are more frequently observed in dogs. This case underscores the need for heightened awareness of amiodarone-induced hypersensitivity reactions in veterinary medicine, particularly in IV formulations. Pre-medication strategies, controlled infusion rates, and close monitoring are essential to mitigating the risk of life-threatening anaphylaxis in human and canine patients. Further research is needed to better understand species-specific differences in amiodarone metabolism and toxicity.
Keywords: Amiodarone, anaphylaxis triggers, Chihuahua dog, hypersensitivity
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Comparative study of pathomorphological changes in uterus and placenta during pregnancy with positive Omicron and Delta SARS‐CoV‐2 variants |
Research PaperCOVID-19
Comparative study of pathomorphological changes in uterus and placenta during pregnancy with positive Omicron and Delta SARS‐CoV‐2 variants
Tyan TV, and Mardonov JN.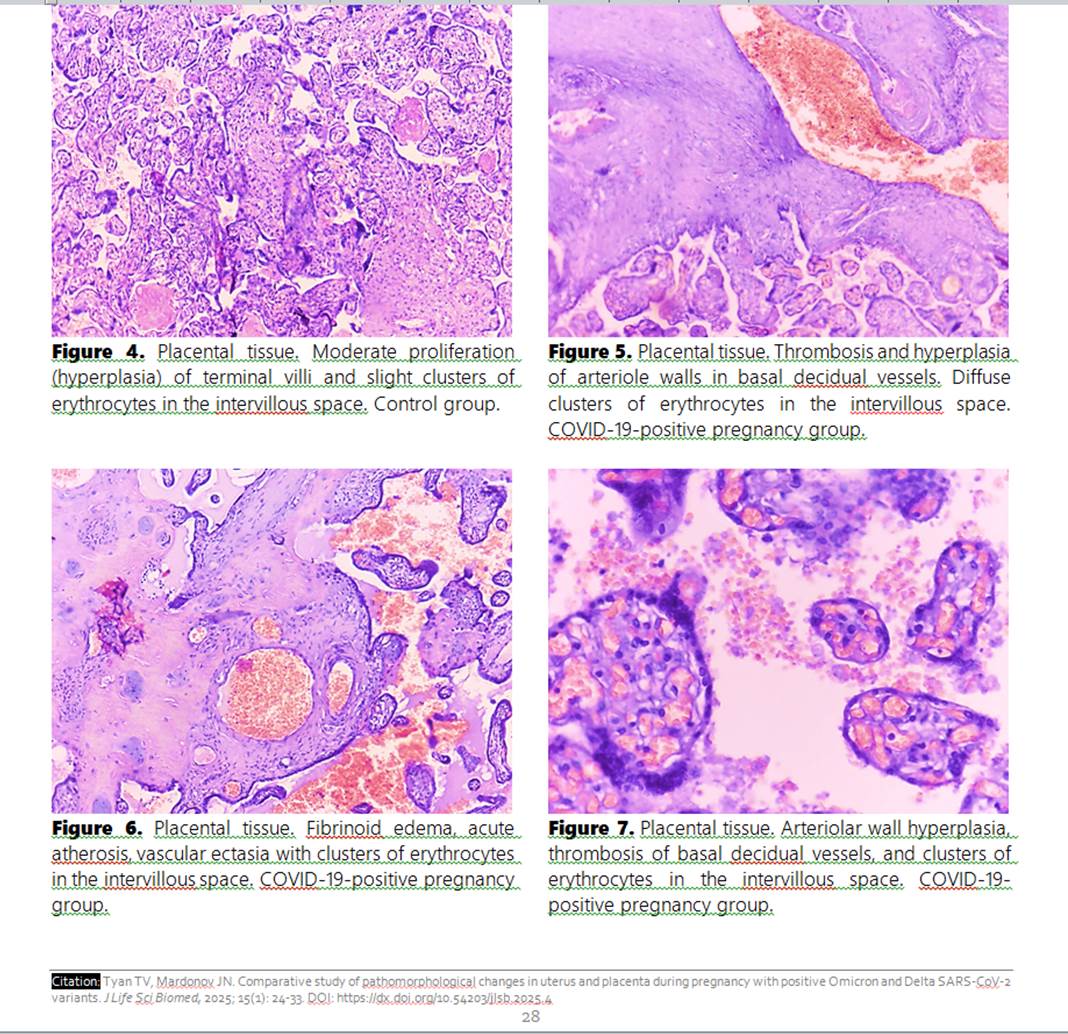 J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 24-33, 2025; pii:S225199392500004-15
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 24-33, 2025; pii:S225199392500004-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.4
Abstract
In recent years, numerous studies have been conducted to examine the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy; however, the pathomorphological changes in the uterus and placenta during this infection remain under-researched. This study aimed to evaluate pathomorphological changes in the uterus and placenta of pregnant women with positive COVID-19 results compared to a non-infected control group. A prospective analytical study including 48 pregnant women tested positive for COVID-19 (24 cases with Delta and 24 Omicron variants) and 42 pregnant women in the control group was conducted. Placental and uterine samples were analyzed using standard histological methods. Results indicated that pregnant women with COVID-19 showed a significant increase in the frequency of retroplacental hematomas, villous hypoplasia, vascular ectasia, and other histopathological changes in the uterus and placenta, especially in women tested positive for Delta variant. This study underscores that Delta SARS‐CoV‐2 variant is associated with marked pathological changes in the placenta and uterus, highlighting the need for careful clinical management in such pregnancies.
Keywords: COVID-19, Delta (B.1.617.2) variant, Omicron (B.1.1.529), pathomorphology, placenta, pregnancy, SARS-CoV-2, uterus.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Health benefits of snail farming in Imo state, Nigeria: a life science and biomedical approach |
Research Paper
Health benefits of snail farming in Imo state, Nigeria: a life science and biomedical approach
Anyiam KH, Nwosu FO, Nwaiwu IUO, Kadiri FA, Obinna-Nwandikom CO, Osuji MN, Anyanwu UG, Enoch OC, Isaiah GI, Bala MB, Obasi AC, Madu JA, and Nnorom EI.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 15(1): 34-41, 2025; pii:S225199392500005-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2025.5
Abstract
Snail farming links food production, life sciences, and biomedicine, offering not only economic benefits but also vital health advantages. This study investigated the health benefits of snails, described the socioeconomic characteristics of snail farmers, compared the price elasticity of demand for snails with other animal proteins, and identified the key factors influencing profitability in snail farming within the study area. Data were collected through a well-structured questionnaire for 150 selected respondents using snowball sampling techniques. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the elasticity model, the profit model, and ordinary least squares multiple regression. The results showed that 51.33% of respondents were male and 48.67% were female, with a mean age of 46 years, mean 6.8 persons per household, mean farming experience of 5.7 years, and 52.22% of respondents engaged in snail farming as their primary occupation. The price elasticity of demand for animal proteins was calculated, resulting in -0.24 for Archantina archantina and -1.10 for Archantina marginata. Snails were found to offer notable health benefits, including low cholesterol content, potential in asthma management, essential vitamins that aid in skincare and nutrients that support brain cell maintenance. The cost and return analysis revealed that a total of $235.67 was incurred, while $647.60 was realized from sales, resulting in a total profit of $411.92. Additionally, the factors affecting the profit of snail farmers were identified, including age, labour, stock size, and feed. The study recommended government intervention to scale up snail production and suggested that stakeholders in the snail industry adopt measures to promote both the production and consumption of snails.
Keywords: Demand, health benefit, profit determinants, snail production.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)