Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 14 (4); December 25, 2024
Volume 14 (4); December 25, 2024
| Molecular characterizations of Toxoplasma gondii among pregnant women attending antenatal care at central Gondar zone public hospital, Northwest Ethiopias |
Research Paper
Molecular characterizations of Toxoplasma gondii among pregnant women attending antenatal care at central Gondar zone public hospital, Northwest Ethiopia
Meressa EW, Atanaw MB, Bicha MM, Eshetu MA, Abebe FK, Admasu AE, Kebede ML, Melese TS, and Tessemma NB.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 14(4): 87-98, 2024; pii:S225199392400009-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.9
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii parasite that causes severe clinical problems such as congenital toxoplasmosis is a major public health problem that affects one-third of the world’s populationand is also associatedwith a high socioeconomic impact for pregnant women. Molecular characterizations for genotyping using PCR for the detection of T. gondii genotyping were grouped into three subtypes, designated I, II, and III, based on polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP).This study aimed to determine molecular characterizations of T. gondii among pregnant women attending Anti-Natal Care (ANC) at Central Gondar Zone Public Hospitals (CGZPH), Northwest Ethiopia. Between 2022 and 2024, a cross-sectional study design was conducted to determine the molecular characterizations of T. gondii among pregnant women attending ANC at CGZPH. In this study, We determined the B1 and Surface antigen 2(SAG2) genotypes of T. gondii in pregnant women using PCR-RFLP. The genotyping data were coded for all genetic loci. Our research provides baseline information essential for planning and implementing control and prevention strategies, thereby enhancing the knowledge and epidemiology of toxoplasmosis. The study revealed that the T. gondii population in the Central Gondar Zone is predominantly represented by type II strains, which are most commonly associated with human toxoplasmosis. The use of PCR-RFLP at the SAG2 and B1 loci proved to be efficient method for rapid genotyping.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii, Molecular characterization, Pregnant women, Ethiopia
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Horizontal gene transfer: the hidden hazards of genetic engineering |
Review
Horizontal gene transfer: the hidden hazards of genetic engineering
Meressa EW and Tseha BA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 14(4): 99-108, 2024; pii:S225199392400010-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.10
Abstract
Horizontal or lateral gene transfer involves to the movement of genetic material between organisms in a manner that is not associated with traditional reproduction. This process can occur through direct methods or via vectors, and it contrasts with vertical gene transfer, where genes are passed to offspring. Genetic engineering often utilizes artificial constructs to cross species barriers and integrate in to genomes, facilitating unregulated horizontal gene transfer. These constructs which typically include genetic elements, can naturally mediate horizontal gene transfer. This can lead to the spread of diseases, antibiotic resistance, and even cancer in mammalian cells. Given these risks, it is crucial to establish effective regulatory measures to prevent the release of these constructs into the environment and to consider the continuation of potentially hazard experiments. This review aims to highlight the current status and implications of horizontal gene transfer facilitated by genetic engineering, emphasizing the need for stringent regulatory measures to mitigate associated risks.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance, artificial vector, dormant viruses, CaMV promoter, naked DNA, transgenic DNA
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
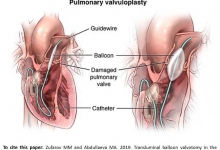
| Assessment of long-term hemodynamic changes following balloon valvuloplasty for pulmonary artery stenosis |
Research Paper
Assessment of long-term hemodynamic changes following balloon valvuloplasty for pulmonary artery stenosis
Zufarov MM, Umarov MM, and Ibadov RR.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 14(4): 109-115, 2024; pii:S225199392400011-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.11
Abstract
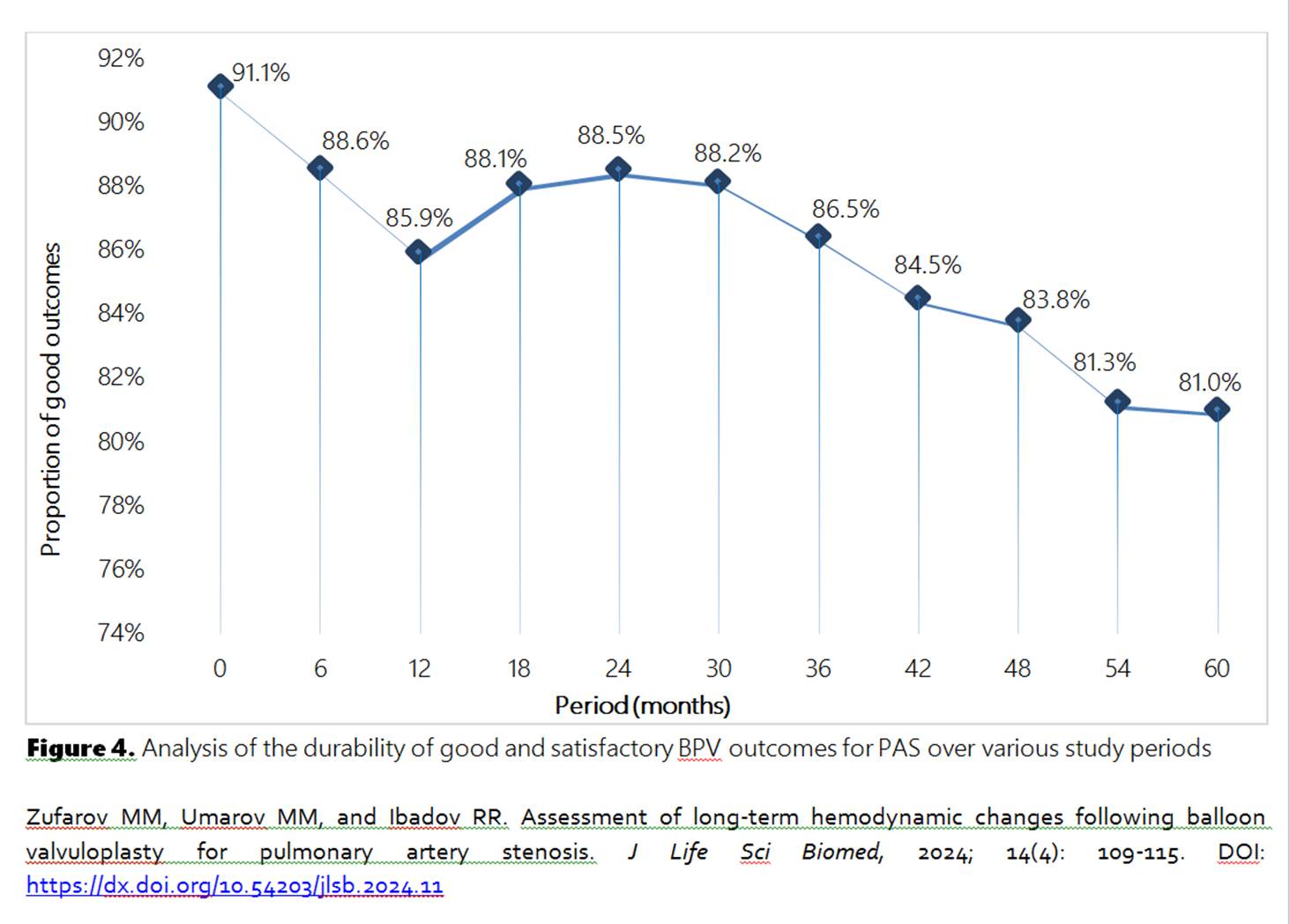
Pulmonary artery stenosis (PAS) is a common congenital heart defect with a significant impact on the cardiovascular health of affected patients. Despite advancements in interventional cardiology, the long-term hemodynamic outcomes following balloon valvuloplasty (BV) for PAS remain insufficiently studied, especially in varying clinical and demographic subgroups. This knowledge gap necessitates further investigation. To assess long-term hemodynamic changes in patients with PAS after BV and analyze factors contributing to unsatisfactory outcomes. This single-center retrospective cohort study included 180 patients with PAS who underwent BV at the RSPPMCS named after Acad. V. Vakhidov between 2010 and 2022. Patients were categorized based on PAS type and baseline right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). Hemodynamic parameters were assessed using echocardiography and CT angiography. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis evaluated the durability of good and satisfactory outcomes. Statistical comparisons were made using t-tests and multivariate regression analysis, with p-values reported to three decimal places. Among the 180 patients, 144 (80.0%) had isolated valvular PAS, 27 (15.0%) had combined valvular-subvalvular PAS, and 9 (5.0%) had valvular-supravalvular PAS. Initial mean RVSP was 93.4±6.7 mmHg, which decreased significantly to 25.3±3.2 mmHg immediately post-BV (p<0.001). Long-term follow-up was achieved in 58 patients over five years, with mean RVSP stabilizing at 26.2±2.4 mmHg. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that 81.0% of patients maintained good outcomes at five years. Predictors of poor outcomes included inadequate balloon-to-annulus ratio (<1.2) and residual gradients ≥50 mmHg. Repeat BV improved outcomes in 100% of re-treated cases. BV demonstrates high efficacy in the long-term management of PAS, with sustained improvement in hemodynamics observed in most patients. Optimal balloon sizing remains critical to reducing residual gradients and ensuring long-term success. Further studies should explore additional predictors of restenosis to refine patient selection and procedural strategies.
Keywords: Pulmonary artery stenosis; balloon valvuloplasty; hemodynamic outcomes; congenital heart defects; long-term follow-up.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Evaluating the sensitivity and specificity of a rapid antigen screening test against real-time polymerase chain reaction for COVID-19 detection in northern Ethiopia |
Research PaperCOVID-19
Evaluating the sensitivity and specificity of a rapid antigen screening test against real-time polymerase chain reaction for COVID-19 detection in northern Ethiopia
Abebe B, Birhane N, Girmay G, Belete D.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 14(4): 116-127, 2024; pii:S225199392400012-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.12
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2024.12
Abstract
Early diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19-positive patients are crucial to limiting complications and transmission. Despite real-time PCR being considered a gold standard for the diagnosis of COVID-19, its availability is still limited. There is a paucity of studies that show the sensitivity and specificity of rapid antigen tests (RAT) in Ethiopia. This study aimed to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of rapid antigen tests for the diagnosis of sever acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type-2 (SARS-COV-2 among COVID-19 suspected patients. A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted on COVID-19-positive and negative individuals in the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital from December 26, 2022, to April 30, 2023. Socio-demographic, behavioral, and clinical data were collected using a structured questionnaire. All nasopharyngeal or throat swabs were tested using the PanbioTM COVID-19 rapid antigen test and the BIO-RAD CFX connectTM reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Sensitivity, specificity, Kappa, and positive and negative predictive values were analyzed using the online Medcalc statistical tool to determine the diagnostic performance of the rapid antigen test using the RT-PCR reference method. Out of 120 participants, 53.3% were female. In this study, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the PanbioTM rapid antigen test were 98.36%, 100%, and 98.33%, respectively The positive and negative predictive values were 100% and 99.17%, respectively. The Kohen’s kappa statistic was 0.983 at 50% estimation of the disease prevalence. PanbioTM rapid antigen test resulthowed outstanding agreement with RT-PCR using a nasopharyngeal or nasal swab from symptomatic patients. The RAT affordable and provides immediate outcome with in short period of time. In order to quickly identify the positive cases and put isolation and infection control measure in place, this test can be used in regions where the numbers SARS-CoV-2 cases is fast increasing.
Keywords: COVID-19, diagnostic performance, PanbioTM, rapid antigen test
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)